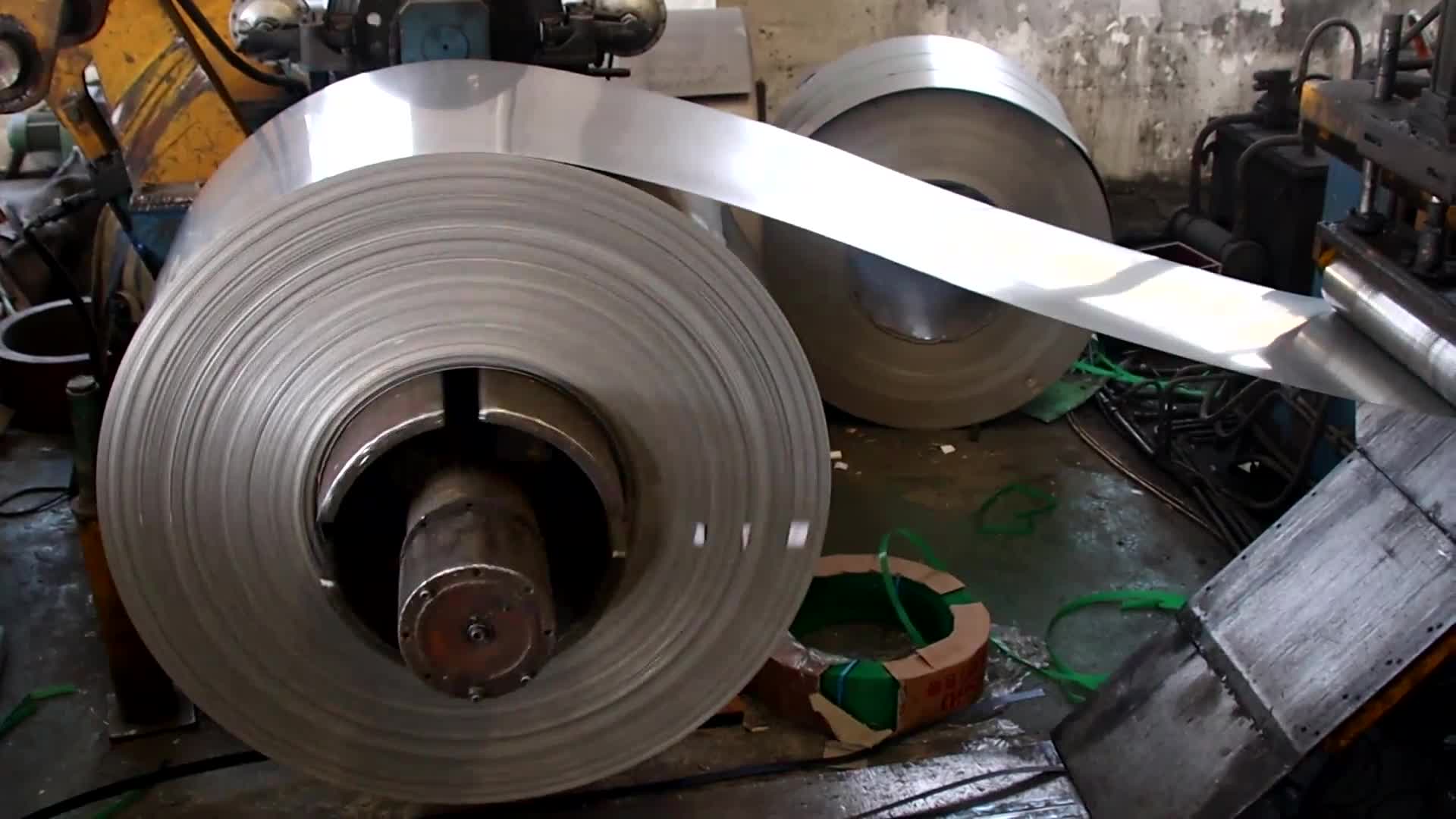
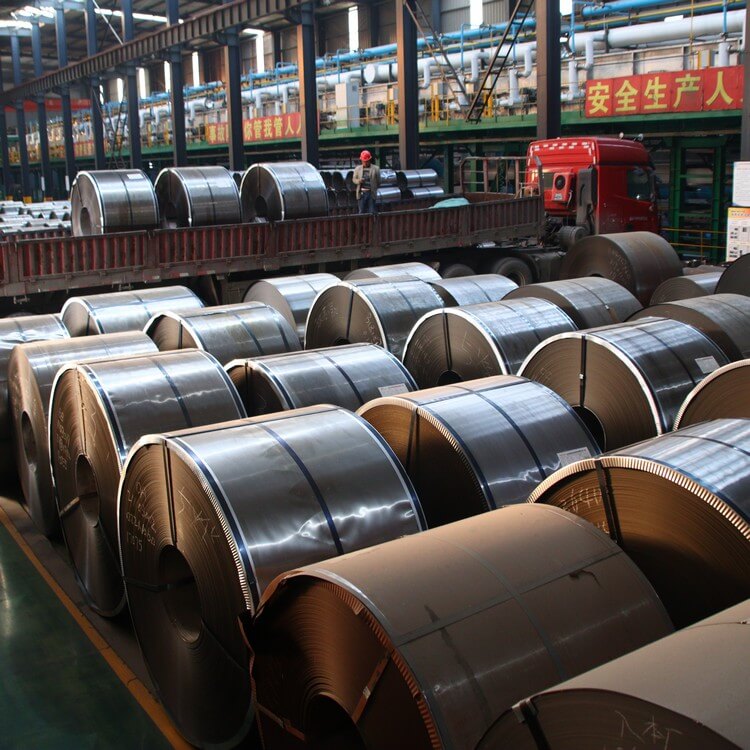
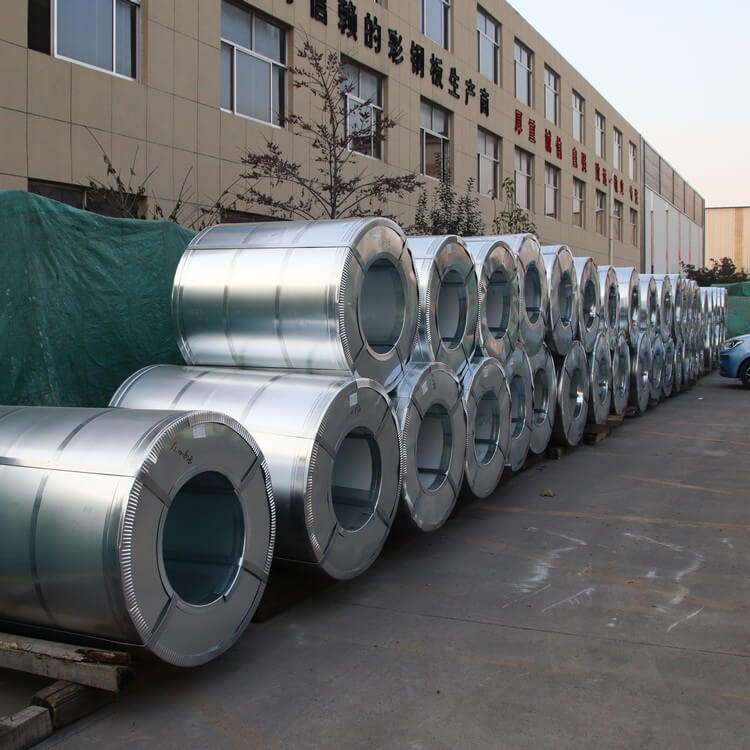
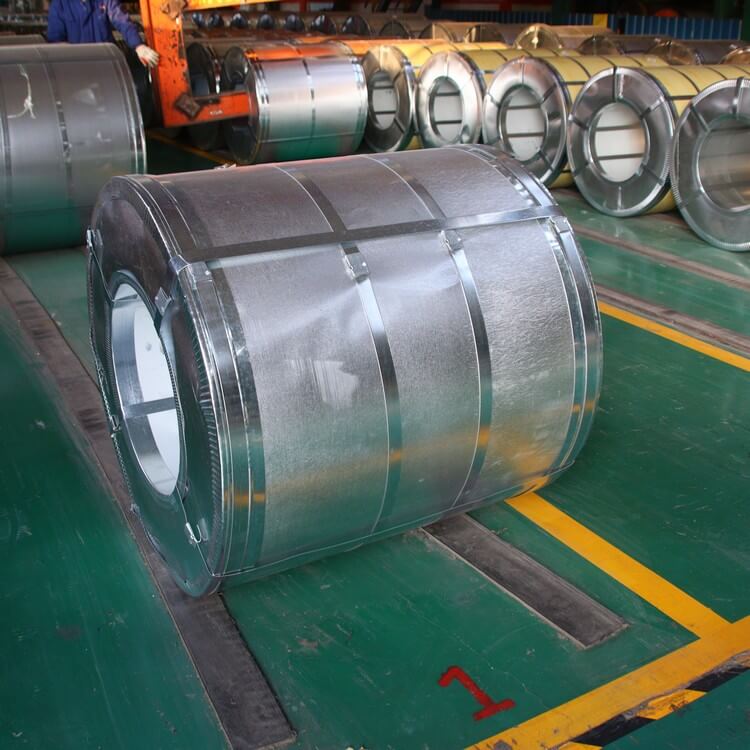




321 stainless steel has excellent high temperature stress rupture performance and high temperature creep resistance stress mechanical properties.
advantage
stainless steel coil is also called coil strip, coil material, coil plate, plate coil, and the hardness of the strip is also many.
The stainless steel coil is simply an extension of the ultra-thin stainless steel plate. It is mainly a narrow and long steel plate produced to meet the needs of industrialized production of various metal or mechanical products in different industrial sectors.
Features of stainless steel belt:
1. Complete product specifications and various materials;
2. High dimensional accuracy, up to ±0.1mm;
3. Excellent surface quality and good brightness;
4. Strong corrosion resistance, high tensile strength and fatigue resistance;
5. The chemical composition is stable, the steel is pure, and the inclusion content is low;
6. Well packaged and favorable price;
7. Can be customized.
Stainless steel belt classification:
There are many types of stainless steel belts, which are widely used: 201 stainless steel belts, 202 stainless steel belts, 304 stainless steel belts, 301 stainless steel belts, 302 stainless steel belts, 303 stainless steel belts, 316 stainless steel belts, J4 stainless steel belts, 309S stainless steel belts, 316L stainless steel belts, 317L stainless steel belt, 310S stainless steel belt, 430 stainless steel iron belt, etc.
Stainless steel belt: stainless steel coil belt, stainless steel spring belt, stainless steel stamping belt, stainless steel precision belt, stainless steel mirror belt, stainless steel cold rolled belt, stainless steel hot rolled belt, stainless steel etching belt, stainless steel stretching belt, stainless steel polishing belt, stainless steel soft belt , stainless steel hard belt, stainless steel medium hard belt, stainless steel high temperature belt, etc.
Cold rolled stainless steel coil:
1. Using "stainless steel coil/coil" as raw material, it is rolled into products by cold rolling mill at room temperature. Conventional thickness <0.1mm~3mm>, width <100mm~2000mm>;
2. ["Cold-rolled steel strip/coil"] has the advantages of smooth surface, smooth surface, high dimensional accuracy and good mechanical properties, and most of the products are in coils, which can be processed into coated steel plates;
3. Production process of cold-rolled stainless steel coil/coil: 1.Pickling → 2.Rolling at room temperature →3.Process lubrication → 4. Annealing → 5.Flattening → 6.Fine cutting →7. Packaging → 8.Reach customers.
hot rolled strip
1. A strip with a thickness of 1.80mm-6.00mm and a width of 50mm-1200mm is formed by a hot rolling machine.
2.【Hot-rolled strip/sheet】has the advantages of low hardness, easy processing and good ductility.
3. Hot-rolled stainless steel coil/coil production process: 1.pickling →2.high temperature rolling →3.process lubrication →4.annealing →5.smoothing →6.fine cutting →7.packaging →8.to reach the customer.
difference between hot and cold
1. Cold-rolled steel strip has good strength and yield ratio, and hot-rolled steel strip has good ductility and toughness.
2. The surface quality, appearance and dimensional accuracy of cold-rolled steel strips are better than those of hot-rolled steel strips.
3. The thickness of cold-rolled steel strip is ultra-thin, and the thickness of hot-rolled steel strip is larger.
Silicon steel strip
The grain-oriented silicon steel strip is also called the cold-rolled silicon steel strip for the telecommunication industry. Silicon steel strips larger than 0.20mm.
cold rolled strip
Cold-rolled steel strip for deep drawing is a low-carbon high-quality carbon structural steel cold-rolled steel strip used for deep drawing of complex drawn parts.
delivery status:
Delivery after heat treatment and smoothing.
The surface of the steel strip as supplied shall be rough or bright.
Usage: Widely used in automobiles, tractors and other industrial applications.
delivery status:
Delivered in the state of heat treatment (annealing, normalizing, tempering after normalizing, high temperature tempering).
The steel strip can be delivered without heat treatment under the condition that all properties meet the standard requirements. Ordinary drawing grade steel strips are allowed to be delivered without heat treatment.
The cold-rolled steel strip is delivered in the state of heat treatment (annealing, normalizing, and tempering after normalizing), and should be delivered flat.
Usage:
Widely used in the automotive industry, aviation industry and other sectors, with a large amount of use.
principle
When the steel or sample is stretched, when the stress exceeds the elastic limit, even if the stress does not increase, the steel or sample continues to undergo obvious plastic deformation, which is called yielding, and the minimum stress value when the yielding phenomenon occurs is for the yield point. Let Ps be the external force at the yield point s, and Fo be the cross-sectional area of the sample, then the yield point σs =Ps/Fo(MPa), MPa is called MPa, which is equal to N (Newton)/mm2, (MPa=106Pa, Pa: Pascal =N/m2).
performance
Like other materials, the physical properties of stainless steel coil mainly include the following three aspects: thermodynamic properties such as melting point, specific heat capacity, thermal conductivity and linear expansion coefficient, electromagnetic properties such as resistivity, electrical conductivity and magnetic permeability, and Young's modulus of elasticity , stiffness coefficient and other mechanical properties. These properties are generally considered to be inherent properties of stainless steel materials, but are also affected by factors such as temperature, degree of processing and magnetic field strength. Generally speaking, stainless steel has lower thermal conductivity and higher resistance than pure iron, and the properties such as linear expansion coefficient and magnetic permeability vary according to the crystal structure of stainless steel itself.
Product Details
Dependence of physical properties on temperature
1.Specific heat capacity
The specific heat capacity will change with the change of temperature, but once the phase transition or precipitation occurs in the metal structure during the temperature change, the specific heat capacity will change significantly.
2.Thermal conductivity
Below 600℃, the thermal conductivity of various stainless steels is basically in the range of 10~30W/(m·℃), and the thermal conductivity tends to increase with the increase of temperature. At 100℃, the order of thermal conductivity of stainless steel from large to small is 1Cr17, 00Cr12, 2 Cr 25N, 0 Cr 18Ni11Ti, 0 Cr 18 Ni 9, 0 Cr 17 Ni 12Mο2, 2 Cr 25Ni20. The order of smallest is 1 Cr 13, 1 Cr 17, 2 Cr 25N, 0 Cr 17Ni12Mο2, 0 Cr 18Ni9Ti and 2 Cr 25Ni20. The thermal conductivity of austenitic stainless steel is slightly lower than that of other stainless steels. Compared with ordinary carbon steel, the thermal conductivity of austenitic stainless steel at 100 °C is about 1/4.
3.Linear expansion coefficient
In the range of 100-900°C, the linear expansion coefficients of the main grades of various stainless steels are basically 10ˉ6~130*10ˉ6°Cˉ1, and show an increasing trend with the increase of temperature. For precipitation hardening stainless steel, the size of the linear expansion coefficient is determined by the aging treatment temperature.
4.Resistivity
At 0~900℃, the specific resistance of various stainless steel grades is basically 70*10ˉ6~130*10ˉ6Ω·m, and it tends to increase with the increase of temperature. When used as a heating material, materials with low resistivity should be selected.
5.Magnetic permeability
The magnetic permeability of austenitic stainless steel is extremely small, so it is also called non-magnetic material. Steels with stable austenitic structures, such as 0 Cr 20 Ni 10, 0 Cr 25 Ni 20, etc., will not be magnetic even if they are processed with a large deformation of more than 80%. In addition, high carbon, high nitrogen, high manganese austenitic stainless steel, such as 1Cr17Mn6NiSN, 1Cr18Mn8Ni5N series and high manganese austenitic stainless steel, etc., will undergo phase transformation under large reduction machining conditions, so it remains non-magnetic. At high temperatures above the Curie point, even strongly magnetic materials lose their magnetic properties. However, some austenitic stainless steels such as 1Cr17Ni7 and 0Cr18Ni9, because of their metastable austenite structure, will undergo martensitic transformation during large-reduction cold working or low-temperature working, and they will be magnetic and magnetic. Conductivity will also increase.
6.Elastic modulus
The longitudinal elastic modulus of ferritic stainless steel at room temperature is 200 kN/mm2, and the longitudinal elastic modulus of austenitic stainless steel is 193 kN/mm2, which is slightly lower than that of carbon structural steel. As the temperature increases, the longitudinal elastic modulus decreases, the Poisson's ratio increases, and the transverse elastic modulus (stiffness) decreases significantly. The longitudinal elastic modulus will have an effect on work hardening and tissue aggregation.
7.Density
Ferritic stainless steel with high chromium content has low density, and austenitic stainless steel with high nickel content and high manganese content has high density. At high temperature, the density becomes smaller due to the increase of the lattice spacing.
Physical properties at low temperature
1.Thermal conductivity
The thermal conductivity of various stainless steels at extremely low temperatures is slightly different, but in general it is about 1/50 of the thermal conductivity at room temperature. Thermal conductivity increases with increasing magnetic flux (magnetic flux density) at low temperatures.
2.Specific heat capacity
At very low temperatures, there are some differences in the specific heat capacity of various stainless steels. The specific heat capacity is greatly affected by temperature, and the specific heat capacity at 4K can be reduced to less than 1/100 of the specific heat capacity at room temperature.
3.Thermal expansion
For austenitic stainless steel, the shrinkage rate (relative to 273K) is slightly different below 80k. The content of nickel has a certain influence on the shrinkage rate.
4.Resistivity
The difference in resistivity between the grades increases at very low temperatures. Alloying elements have a great influence on the resistivity.
5.Magnetic
At low temperature, the influence of the mass magnetic susceptibility of austenitic stainless steel on the load magnetic field is different depending on the material. The content of different alloying elements is also different.
There is no difference in the permeability of different grades.
6.Elastic modulus
At low temperature, the Poisson's ratio of the magnetically transformed austenitic stainless steel produces extreme values accordingly.
Product Parameters
| Grade | C | Si | Mn | P≤ | S≤ | Cr | Mo | Ni | Other |
| 321 | ≤0.12 | ≤1.00 | ≤2.00 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 17-19 | - | 9 | Ti≥5×C |
| Grade | YS(Mpa) ≥ | TS (Mpa) ≥ | El (%) ≥ | Hardness(HV) ≤ |
| 321 | 200 | 520 | 40 | 180 |
Commodity | Austenitic, Ferritic, Martensitic, Duplex, Cold rolled, Hot rolled | |||
Grade | 201, 202, 301, 304, 304j1, 304l, 321, 309s, 310s, 2205, 409l, 410, 410s, 420, 420j1, 420j2, 430, 439, 409l, 443, 444, etc | |||
Standard | ISO, JIS, ASTM, AS, EN, GB | |||
Surface | N0.1, N0.2, N0.3, N0.4, N0.5, N0.6, N0.7, N0.8, 2D, 2B, HL, BA, 6K, 8K, etc | |||
Thickness | 0.1-200mm | |||
Width | 10-2000mm | |||
MOQ | 1T | |||
Packaging | Export standard, seaworthy | |||
Trade Term | FOB, CFR, CIF | |||
Transport Type | Container, bulk and train | |||
Loading port | qingdao, tianjin, etc | |||
Payment terms | T/T, L/C at sight,West Union,D/P,D/A,Paypal | |||
Delivery time | 15-35 days after confirmed order | |||
 Product catalogue
Product catalogue
 Hot Products
Hot Products
Request a Quote
TISCO Steel is a comprehensive enterprise integrating steel trade, processing. Providing one-stop service for global customers. Complete specifications,Export to the world, Factory direct sales, Integrity management. Meet all your steel needs!
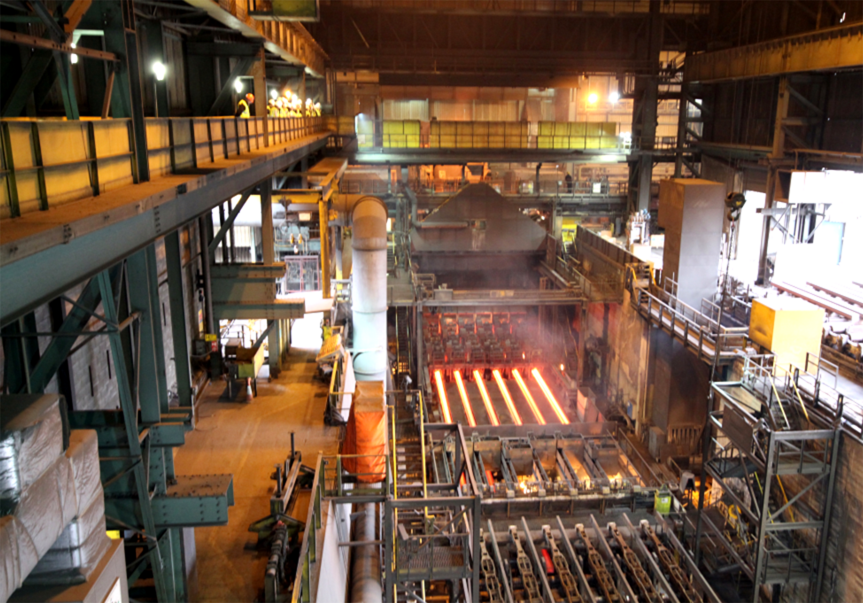
Strong technical force.
Sophisticated production equipment.
Strict quality control procedures assuring the highest quality products.
Professional technical team and experienced project management team.
Inventory large shipment loss ah, price concessions complete specificationsto meet all your steel needs.















We are a well known worldwide exporter of Aluminum coils, Ireland, Portugal, Gambia, Thailand, Ukraine, United Kingdom, Netherlands, South Africa, Spain, Turkey, Italy, Libya, Romania, Puerto Rico, Azerbaijan, United Arab Emirates, Pakistan, Philippines, Ghana, Slovakia, Germany, Saudi Arabia, Afghanistan, China, Bolivia, Switzerland, Bangladesh, Taiwan, Oman, Egypt, Greece, Norway, Singapore, Bulgaria, Estonia, Belgium, Yemen, Hong Kong, Ecuador, Sri Lanka, Nepal, Belarus, Finland, Gabon, Iran, Canada, Argentina, Lebanon.
Commodity | Austenitic, Ferritic, Martensitic, Duplex, Cold rolled, Hot rolled | |||
Grade | 201, 202, 301, 304, 304j1, 304l, 321, 309s, 310s, 2205, 409l, 410, 410s, 420, 420j1, 420j2, 430, 439, 409l, 443, 444, etc | |||
Standard | ISO, JIS, ASTM, AS, EN, GB | |||
Surface | N0.1, N0.2, N0.3, N0.4, N0.5, N0.6, N0.7, N0.8, 2D, 2B, HL, BA, 6K, 8K, etc | |||
Thickness | 0.1-200mm | |||
Width | 10-2000mm | |||
MOQ | 1T | |||
Packaging | Export standard, seaworthy | |||
Trade Term | FOB, CFR, CIF | |||
Transport Type | Container, bulk and train | |||
Loading port | qingdao, tianjin, etc | |||
Payment terms | T/T, L/C at sight,West Union,D/P,D/A,Paypal | |||
Delivery time | 15-35 days after confirmed order | |||
Tianjin TISCO has extensive industry experience, an expert staff, and state-of-the-art equipment. Our team ensures your material meets your exact specifications and is delivered just when you need it.
 Tel: +86 13370586666
Tel: +86 13370586666  E-mail:[email protected]
COPY
E-mail:[email protected]
COPY
 Leave a message
Leave a message